In this article, you will learn the concept of C strcpy() and strncpy() standard library function defined under string handling library <string.h>.

This standard library functions copy the content of one string into another.
Please visit C programming string to learn more about string.
C strcpy() and strncpy() : Function Prototype
char *strcpy( char *str1, const char *str2)
char *strncpy( char *str1, const char *str2, size_t n)where,
str1 = destination string or character array.
str2 = source string.
The strcpy function copies string str2 into array str1 and returns the value of str1.
On the other hand, strncpy copies the n characters of string str2 into array str1 and returns the value of str1.
str2 may be a character array variable or directly string.
'\0'.
strncpy does not always copy terminating null character '\0'. It depends upon the value of n, if it is at least one more than the length of the string str2 the terminating null character is copied.
Program to demonstrate the function of C strcpy() and strncpy()
/*C program to demonstrate the function of strcpy and strncpy*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
int main()
{
char str1[ ] = "Hello World !!!";
char str2[ 20 ];
char str3[ 10 ];
//printing array str1
printf("\nstr1 = %s", str1);
//copying string directly to array str2
printf("\n\nstr2 = %s", strcpy(str2, "trytoprogram"));
//copying character array str1 to str2
printf("\n\nstrcpy(str2, str1) = %s", strcpy(str2, str1));
//copying first 9 characters of str1 to str3
strncpy(str3, str1, 9);
str3[ 9 ] = '\0'; //putting terminating character at the end
//printing str3
printf("\n\nstrncpy(str3, str1, 9) = %s\n", str3);
return 0;
}
Output
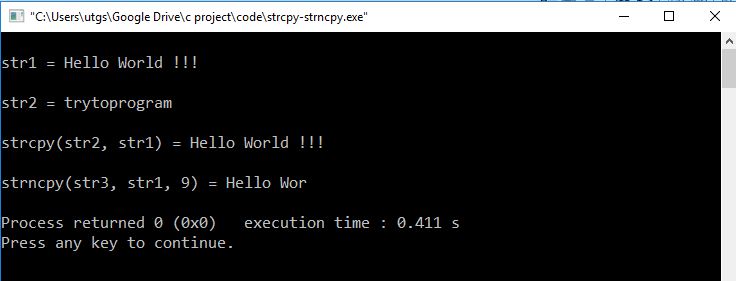
Explanation
In the above program, we can see that string "trytoprogram" and character array is copied directly into character array str2.
While using strncpy( ) in the above program, we have explicitly added terminating null character '\0' in the last place as follow:
strncpy(str3, str1, 9);
str3[ 9 ] = '\0';This is done because we have only copied first 9 characters and there is no terminating null character at the end of character array str3.

