In this article, you will learn about C string library function memmove() with detail explanation and example.

memmove() is related to memory operation that is defined under string header library string.h. Therefore we should include string.h before using it.
#include<string.h>Function prototype of C string library function memmove()
void *memmove( void *str1, const void *str2, size_t n );where,
str1 = Pointer to the destination array or object where content will be copied
str2 = Pointer to the source array or object from where content will be copied
n = size of content to be copied in bytes
Like memcpy, this function also copies n number of bytes from the memory block pointer by str2 into str1 and returns a pointer to the memory location.
The only difference is that copying is performed as if the characters were first copied into temporary memory location then copied into memory block pointed by str1.
As a result, we are able to copy the particular part of a string into another part of the same string.
Program to demonstrate the use of C string library function memmove()
/*Use of string library function memmove*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
int main()
{
//declaring and initializing character array
char str1[ ] = "Learn C from trytoprogram.com";
char str2[ ] = "trytoprogram.com";
char str3[ ] = "Hello World !!!";
//displaying str1, str2 and str3
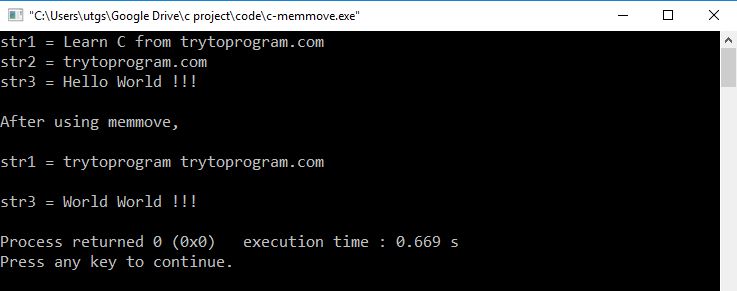
printf("str1 = %s\n", str1);
printf("str2 = %s\n", str2);
printf("str3 = %s\n", str3);
memmove(str1, str2, 12);
memmove(str3, &str3[6], 5);
printf("\nAfter using memmove,\n"
"\nstr1 = %s\n"
"\nstr3 = %s\n", str1, str3);
return 0;
} //endOutput
Explanation
In the first memmove operation, we have copied 12 characters from str2 into str1. This is similar to memcpy( ).
However, in the second memmove operation, we have copied 5 characters from the str3 into the same array.
We cannot perform the second operation using memcpy( ).

