In this tutorial, you will learn about batch file variables and how they are used in batch file programming or scripting. You will also learn about the scope of variables in batch files.
| Batch variables: Syntax |
| Batch variables: Example |
| Global variables vs Local variables |
Batch file variables don’t need a declaration, in fact, the value is directly assigned to a variable using SET command.
Batch file variables – Syntax
Besides some reserved words (these predefined commands should not be used), any word or letter can be used as a variable.
Here is how the batch variables are declared.
SET varibale_name=variable_value
:: for assigning numeric value
SET /A variable_name=nameric_valueNote: DOS or Batch commands are not case sensitive and ‘/A’ is used for assigning numeric values. Uninitialized variables are empty strings in batch files.
Set command overwrites any existing variables. For example, dynamic variables like %DATE% , %TEMP%, %CD% and others seem so fancy that you ought to use these variables. But note that these dynamic variables act like commands in DOS and overwriting these variables can alter their meanings.
So it’s always better to verify you aren’t using any system variables. But how do verify it?
How to verify if batch variables are defined already?
Here is how we can check if a variable is defined or not in DOS.
IF DEFINED MyVar (ECHO MyVar IS defined) ELSE (ECHO MyVar is NOT defined)Go through our batch files if else tutorial, if you are not familiar with the batch file if-else statements.
Batch file variables – Example
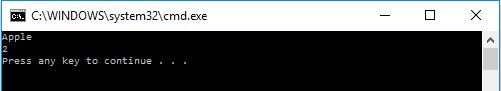
@echo OFF
SET name=Apple
ECHO %name%
:: For numberic variable
SET a=2
ECHO %a%
PAUSEThis script will generate following output:
PAUSE is used to hold the screen until and it waits for user’s input.
SET name=Apple will work but SET name = Apple will not.
Now that you know how variables are used in batch file programs, let’s discuss global and local variables in batch files.
Variable scope in Batch files: Global variables and Local variables
As the name goes, global variable means a variable that can be accessed from anywhere in the program and local variable is the one that has limited scope or can be accessed from locally defined sections. By default, all the variables in batch file programs are GLOBAL.
Like any other programming language, Batch or DOS programming also has a definition for global and local variables.
As we mentioned, by default all the variables are global in a batch script, but they can be used as the local variable by using SETLOCAL command. Any variable assigned in between SETLOCAL and ENDLOCAL is taken as a local variable and its scope terminates and the variable is destroyed as soon as the ENDLOCAL statement is executed.
Following example will clear the concept of the local and global variable in batch file programming.
Example
@echo oFF
SET var1=var1 is global variable
SETLOCAL
SET var2=var2 is a local variable
ECHO %var1%
ECHO %var2%
ENDLOCAL
PAUSEThis will generate following output:

So it works in a cool way.
Now let’s see what happens when we try to use a local variable beyond its scope i.e using after ENDLOCAL.
Example
@echo oFF
SET var1=var1 is global variable
SETLOCAL
SET var2=var2 is a local variable
ECHO %var1%
ENDLOCAL
ECHO %var2%
PAUSEIn this program, var2 is a local variable and when we try to access it after ENDLOCAL is executed, the following happens.

So as seen in this output, when we try to use local variable beyond its scope, instead of executing commands with the local variable, the ECHO is turned off.
